-40%
WW1 FRANCE VICTORY MEDAL SEE STORE WE HAVE WW1-WW2- BADGES-PATCHES MEDALS
$ 21.11
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
PLEASE FOLLOW OUR E BAY STORESEE ALL PICS
SALE
SEE OUR STORE
PLEASE READ WHOLE ADD
SEE STORE !!!!
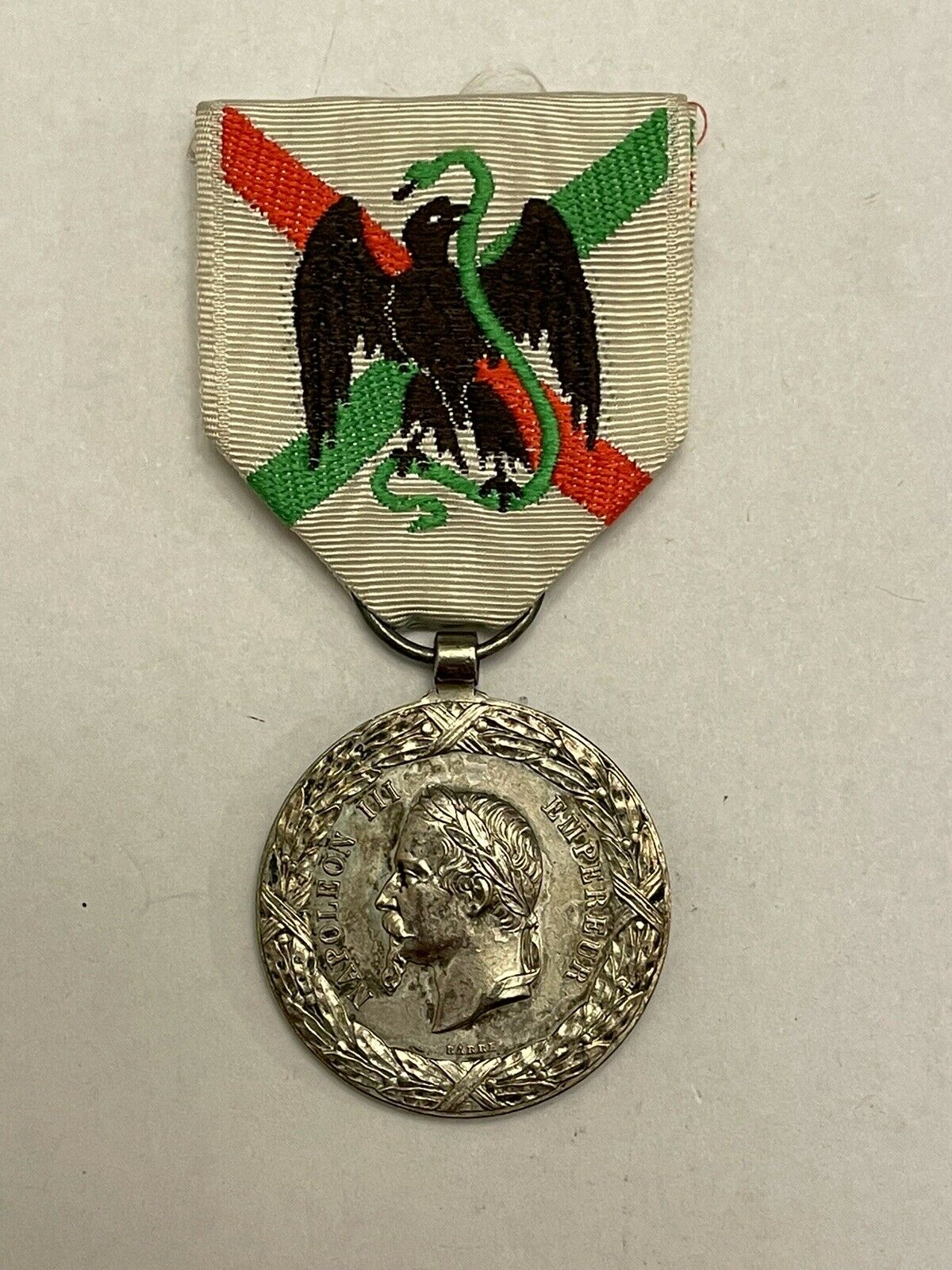
1914–1918 Inter-Allied Victory medal (France)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
1914–1918 Inter-Allied Victory medal (France)
Obverse and reverse of the 1914–1918 Inter-Allied Victory medal
Type
Commemorative Medal
Awarded for
Participation in
World War I
Presented by
France
Eligibility
Allied military forces, and attached civilians
Status
No longer awarded
Established
20 July 1922
Ribbon of the 1914–1918 Inter-Allied Victory medal
Precedence
Next (higher)
Médaille commémorative du Maroc (1909)
Next (lower)
Médaille commémorative de la bataille de Verdun
Related
Médaille commémorative de la guerre 1914–1918
The
1914–1918 Inter-Allied Victory medal
(
French
:
"Médaille Interalliée de la Victoire 1914–1918"
) was a French commemorative medal established on 20 July 1922. It was the French version of a common allied campaign medal where each allied nation issued a Victory Medal to their own nationals, all issues having certain common features, including the same ribbon, a winged figure of victory on the obverse and a similar inscription on the reverse, the French version reading "LA GRANDE GVERRE POUR CIVILISATION 1914-1919".
It was awarded to all soldiers who served three months, consecutive or not, between 2 August 1914 and 11 November 1918 in the war zone. It was also awarded to civilian nurses,
aliens
(civilian or military) who served directly under French command,
Marshals
and generals who had a command for at least three months, prisoners of war from
Alsace
and
Lorraine
who then served in the French forces. Article 10 of the establishing law states: "The right to the medal is also granted to soldiers who were killed by the enemy or died from wounds of war and those (....) who died of disease or injury incurred in service."
[1]
The next of kin of those killed or died were required to procure the medal at their own expense.
[2]
Contents
1
International award
2
Award certificate
3
See also
4
References
International award
[
edit
]
In response to a proposal first made by the French Marshal
Ferdinand Foch
, supreme commander of the Allied Forces during the First World War, most
allied nations
issued a Victory Medal following a common design, thereby avoiding any need for countries to exchange campaign medals.
[3]
Each country produced their own version, following certain common criteria. The medal was to be in bronze with a 36 mm diameter, having a winged figure of victory on the obverse, a common inscription on the reverse and suspension by a double rainbow design ribbon.
[4]
Japan and Siam replaced the figure of victory, since a winged victory symbol was not culturally relevant.
[5]
The following versions were finally awarded:
[6]
At the start of the war in 1914, the countries of Poland and Czechoslovakia were parts of the Russian and Austro-Hungarian Empires respectively.
Country
Designer
Manufacturer
Number issued
Belgium
Paul Du Bois
(1859–1938)
-----
300,000 – 350,000
Brazil
Jorge Soubre (1890–1934)
Casa da Moeda
Rio
approximately 2,500
Cuba
Charles Charles
Etablissements Chobillon
6,000 – 7,000
Czechoslovakia
Otakar Španiel (1881–1955)
Kremnice Mint
approximately 89,500
France
Pierre-Alexandre Morlon (1878–1951)
Monnaie de Paris
approximately 2,000,000
France
[7]
Charles Charles
Etablissements Chobillon
-----
France
[7]
M. Pautot
Louis Octave Mattei
-----
-----
Great Britain
[8]
William McMillan (1887–1977)
Woolwich Arsenal
Wright & Son
5,725,000 plus
[9]
Greece
Henry-Eugène Nocq (1868–1944)
V. Canale
approximately 200,000
Italy
Gaetano Orsolini (1884–1954)
Sacchini-Milano
S.Johnson-Milano
F.M.Lorioli & Castelli-Milano
approximately 2,000,000
Japan
[10]
Shoukichi Hata
Osaka Mint
approximately 700,000
Poland
[11]
... Vlaitov
Mint Kremnica
-----
Portugal
João Da Silva (1880–1960)
Da Costa
approximately 100,000
Rumania
... Kristesko
-----
approximately 300,000
Siam (Thailand)
Itthithepsan Kritakara
(1890–1935)
-----
approximately 1,500
South Africa
[12]
William McMillan (1887–1977)
Woolwich Arsenal
approximately 75,000
United States
James Earle Fraser (1876–1953)
Arts Metal Works Inc.
S.G.Adams Stamp & Stationary Co.
Jos. Mayer Inc.
approximately 2,500,000
(Main source :
The interallied victory medals of world war I
by Alexander J. Laslo, Dorado Publishing, Albuquerque. 1986 Edition )
Award certificate
[
edit
]
A certificate confirming the award was given to each recipient confirming his right to wear the medal.